Researchers at Cambridge University have identified a process called graphitization, which they theorize could produce essential life-building molecules like proteins, phospholipids, and nucleotides on early Earth. This process, highlighted in a study in the journal Life, suggests that the high temperatures resulting from celestial impacts and interactions with iron and water could simplify chemical environments, making them conducive to the formation of life’s necessary components.
Researchers at Cambridge University propose that essential molecules for life’s development might have originated from a process called graphitization. If confirmed through laboratory experiments, this could enable us to simulate conditions that are likely to have led to the emergence of life.
How did the chemicals required for life get there?
It has long been debated how the seemingly fortuitous conditions for life arose in nature, with many hypothesizes reaching dead ends. However, researchers at the University of Cambridge have now modeled how these conditions could occur, producing the necessary ingredients for life in substantial quantities.
Life is governed by molecules called proteins, phospholipids, and nucleotides. Past research suggests that useful molecules containing nitrogen like nitriles – cyanoacetylene(HC3N) and hydrogen cyanide(HCN) – and isonitriles – isocyanide(HNC) and methyl isocyanide(CH3NC) – could be used to make these building blocks of life. As of yet though, there has been no clear way to make all of these in the same environment in substantial amounts.
In a recent study published in Life, the group has now found that through a process known as graphitization, significant quantities of these useful molecules can be theoretically made. If the model can be verified experimentally, this suggests that the process was a likely step for early Earth on its journey toward life.
Why is this process more likely to have occurred than others?
Much of the problem with previous models, is that a range of other products are created along with the nitriles. This makes a messy system that hinders the formation of life.
‘A big part of life is simplicity,’ said Dr Paul Rimmer, Assistant Professor of Experimental Astrophysics at the Cavendish Laboratory, and co-author of the study. ‘It’s order. It’s coming up with a way to get rid of some of the complexity by controlling what chemistry can happen.’
We don’t expect life to be produced in a messy environment. So, what is fascinating is how graphitization itself cleans the environment, since the process exclusively creates these nitriles and isonitriles, with mostly inert side-products.
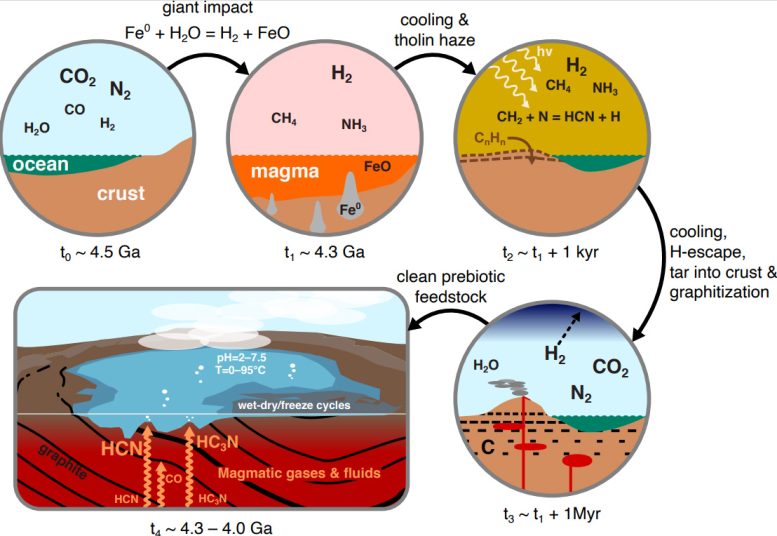
A schematic representation of the scenario we propose here for clean, high-yield production of prebiotic feedstock. Events move around clockwise from the top left: First, the Earth has a neutral atmosphere. This is reduced following a giant impact at 4.3 Ga by oxidation of the impactor’s metal core to produce a massive H2 atmosphere with significant methane and ammonia. This atmosphere quickly cools (in <1 kyr), with photochemistry producing a tholin-rich haze that deposits complex nitrogen-rich organics. These organics become progressively buried and graphitized by interaction with magma. The atmosphere clears as H2 is lost to space and becomes neutral again. Finally, magmatic gases interact with the graphite and are scrubbed to produce high yields of clean HCN, HC3N, and isonitriles. Credit: Oliver Shorttle
‘At first, we thought this would spoil everything, but actually, it makes everything so much better. It cleans the chemistry,’ said Rimmer.
This means graphitization could provide the simplicity scientists are looking for, and the clean environment required for life.
How does the process work?
The Hadean eon was the earliest period in Earth’s history, when the Earth was very different from our modern Earth. Impacts with debris, sometimes the size of planets, were not unheard of. The study theorizes that when the early Earth was hit by an object roughly the size of the moon, around 4.3 billion years ago, the iron that it contained reacted with water on Earth.
‘Something the size of the moon hit early Earth, and it would have deposited a large amount of iron and other metals’ said co-author Dr Oliver Shorttle, Professor of natural philosophy at the Institute of Astronomy and Department of Earth Sciences in Cambridge.
The products of the iron-water reaction condense into a tar on the surface of the Earth. The tar then reacts with magma at over 1500°C and the carbon in the tar becomes graphite- a highly stable form of carbon- and what we use in modern pencil leads!
‘Once the iron reacts with the water, a mist forms that would have condensed and mixed with the Earth’s crust. Upon heating, what’s left is, lo and behold, the useful nitrogen-containing compounds,’ said Shorttle.
What evidence exists to support this idea?
The evidence to support this theory partly comes from the presence of komatiitic rocks. Komatiite is a type of volcanic rock which are formed when very hot magma(>1500°C) cools.
‘Komatiite was originally found in South Africa. The rocks date back to around 3.5 billion years ago,’ said Shorttle. ‘Crucially, we know that these rocks only form at scorching temperatures, around 1700°C! That means the magma would already have been hot enough to heat the tar and create our useful nitriles.’
With the link confirmed, the authors suggest that nitrogen-containing compounds would be made via this method- since we see komatiite, we know the temperature of magma on early Earth sometimes must have been in excess of 1500°C.
What next?
Now experiments must try to recreate these conditions in the lab, and study whether the water, which is inevitably in the system, eats up the nitrogen compounds, breaking them apart.
‘Though we don’t know for sure that these molecules started out life on Earth, we do know that life’s building blocks must be made from molecules that survived in water,’ said Rimmer. ‘If future experiments show that the nitriles all fall apart, then we’ll have to look for a different way.’
Reference: “A Surface Hydrothermal Source of Nitriles and Isonitriles” by Paul B. Rimmer and Oliver Shorttle, 10 April 2024, Life.
DOI: 10.3390/life14040498
The study was funded by Cambridge Planetary Science and Life in the Universe Research Grants.

Dr. Sarah Adams is a scientist and science communicator who makes complex topics accessible to all. Her articles explore breakthroughs in various scientific disciplines, from space exploration to cutting-edge research.