Working from more than 15 billion miles away, NASA engineers have solved a computer problem aboard Voyager 1, allowing the probe to send readable data five months after a chip error made its transmissions impossible to decipher.
Voyager 1, along with its sister craft, Voyager 2, are robotic probes that were launched in 1977. Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in 2012. It’s now 15.1 billion miles away, the farthest from Earth a human-made object has ever traveled.
Learn more: Closer look at Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.
Voyager 2 entered interstellar space − the space between the stars, starting at about 11 billion miles from our sun − in 2018. It’s now 12.7 billion miles away.
Voyager 1’s computer glitch garbled the science and engineering data the craft sends to Earth, which rendered it unreadable. That started on Nov. 14, 2023.
How did engineers fix Voyager’s problem?
Engineers from NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered a single computer chip inside the spacecraft’s Flight Data Subsystem – which collects science and engineering information and transmits it to Earth – had malfunctioned.
Can’t see our graphics? Click here.
The chip stored part of the Flight Data Subsystem’s memory and software code. Engineers could still receive data from Voyager 1, but it was scrambled.
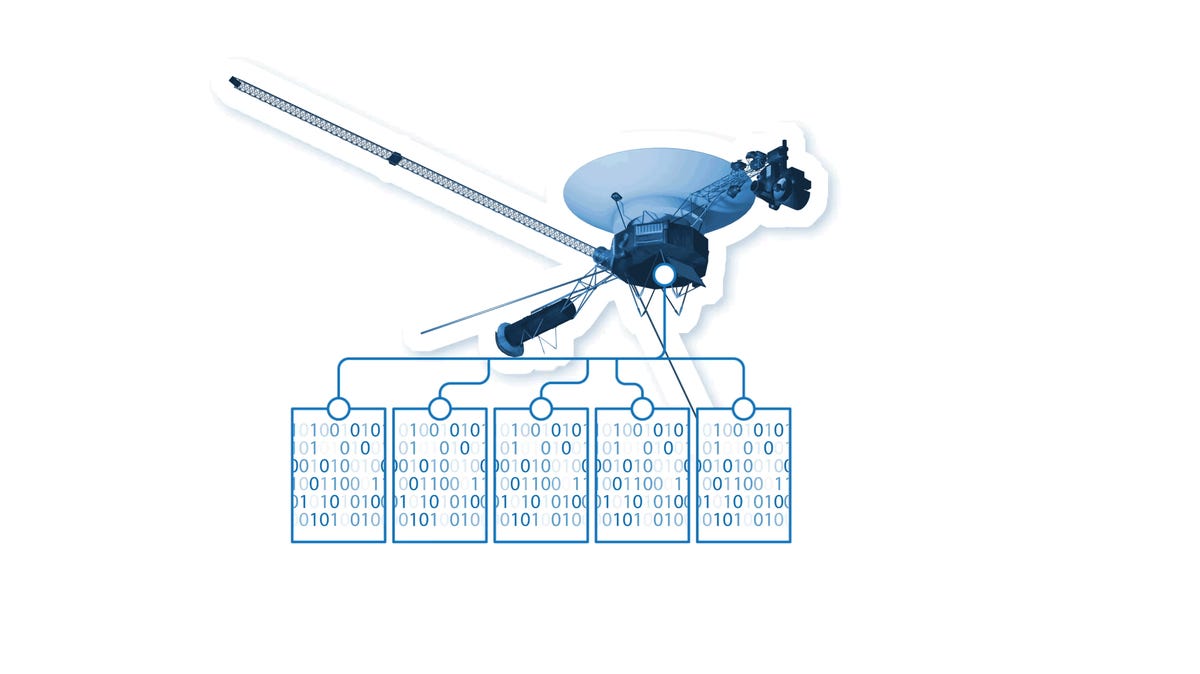
The chip could not be repaired. Instead, engineers moved software code from the chip into a different part of the subsystem’s memory system.
The code was too large to to be stored in a single location in the spacecraft. Engineers divided the code into sections and stored them in different places within the subsystem. The code sections were adjusted to make sure they worked as a whole.
Engineers tested the fix by moving a code that transmits data about the spacecraft. They were rewarded with a transmission from Voyager that contained readable data about the craft’s status.
All that took time. Voyager is moving about 38,000 mph. Because it’s so far away, it takes 22.5 hours for a radio signal to reach Voyager. It takes another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft’s reply to reach antenna networks on Earth.
What happens next?
Engineers will reposition and synchronize the other parts of the code. That should allow Voyager 1 to start sending readable data on what it finds as it moves farther away from Earth.
SOURCE USA TODAY Network reporting and research; NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology; Reuters

Dr. Sarah Adams is a scientist and science communicator who makes complex topics accessible to all. Her articles explore breakthroughs in various scientific disciplines, from space exploration to cutting-edge research.